
Gearing ratios constitute a broad category of financial ratios, of which the D/E ratio is the best known. For example, a prospective mortgage borrower is more likely to be able to continue making payments during a period of extended unemployment if they have more assets than debt. This is also true for an individual applying for a small business loan or a line of credit. If both companies have $1.5 million in shareholder equity, then they both have a D/E ratio of 1. On the surface, the risk from leverage is identical, but in reality, the second company is riskier.
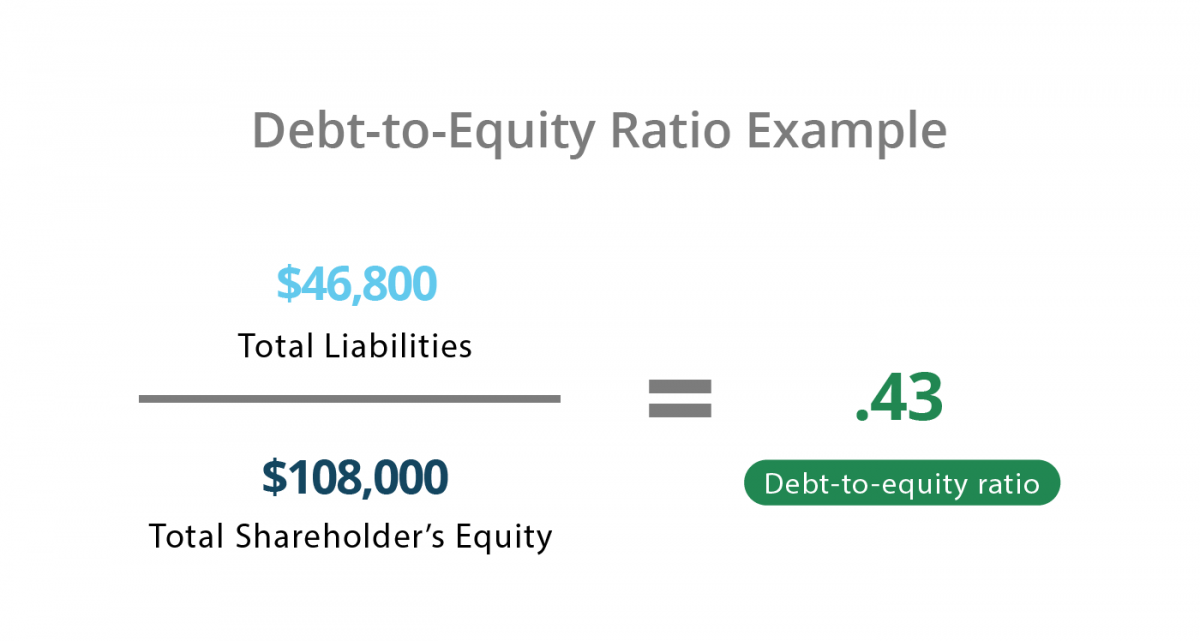
Debt to Equity Ratio Calculation Example
In some cases, the debt-to-equity calculation may be limited to include only short-term and long-term debt. Together, the total debt and total equity of a company combine to equal its total capital, which is also accounted for as total assets. Debt ratio is a metric that measures a company’s total debt, as a percentage of its total assets. A high debt ratio indicates that a company is highly leveraged, and may have borrowed more money than it can easily pay back. Investors and accountants use debt ratios to assess the risk that a company is likely to default on its obligations.
Great! The Financial Professional Will Get Back To You Soon.
Yes, the ratio doesn’t consider the quality of debt or equity, such as interest rates or equity dilution terms. Ultimately, the D/E ratio tells us about the company’s approach to balancing risk and reward. A company with a high ratio is taking on more risk for potentially higher rewards.
- Ultimately, the D/E ratio tells us about the company’s approach to balancing risk and reward.
- A low D/E ratio shows a lower amount of financing by debt from lenders compared to the funding by equity from shareholders.
- The D/E ratio also gives analysts and investors an idea of how much risk a company is taking on by using debt to finance its operations and growth.
- A high Debt to Equity ratio can lead to increased interest expenses and financial instability.
- The term debt ratio refers to a financial ratio that measures the extent of a company’s leverage.
Q. Are there any limitations to using the debt to equity ratio?
A decrease in the D/E ratio indicates that a company is becoming less leveraged and is using less debt to finance its operations. This usually signifies that a company is in good financial health and is generating enough cash flow to cover its debts. The debt-to-equity (D/E) ratio can help investors identify highly leveraged companies that may pose risks during business downturns. Investors can compare a company’s D/E ratio with the average for its industry and those of competitors to gain a sense of a company’s reliance on debt. Including preferred stock in total debt will increase the D/E ratio and make a company look riskier. Including preferred stock in the equity portion of the D/E ratio will increase the denominator and lower the ratio.
A negative D/E ratio indicates that a company has more liabilities than its assets. This usually happens when a company is losing money and is not generating enough cash flow to cover its debts. The D/E ratio also gives analysts and investors an idea of how much risk a company is taking on by using debt to finance its operations and growth. This tells us that Company A appears to be in better short-term financial health than Company B since its quick assets can meet its current debt obligations. When it comes to choosing whether to finance operations via debt or equity, there are various tradeoffs businesses must make, and managers will choose between the two to achieve the optimal capital structure. A higher D/E ratio means that the company has been aggressive in its growth and is using more debt financing than equity financing.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
For the remainder of the forecast, the short-term debt will grow by $2m each year, while the long-term debt will grow by $5m. In addition, the reluctance to raise debt can cause the company to miss out on growth opportunities to fund expansion plans, impact of mobile technology in business communication as well as not benefit from the “tax shield” from interest expense. The other important context here is that utility companies are often natural monopolies. As a result, there’s little chance the company will be displaced by a competitor.
SoFi doesn’t charge commissions, but other fees apply (full fee disclosure here). A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation. Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.
Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master’s in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. Investors may check it quarterly in line with financial reporting, while business owners might track it more regularly. Currency fluctuations can affect the ratio for companies operating in multiple countries.
The debt-to-equity ratio is most useful when used to compare direct competitors. If a company’s D/E ratio significantly exceeds those of others in its industry, then its stock could be more risky. Finally, if we assume that the company will not default over the next year, then debt due sooner shouldn’t be a concern. In contrast, a company’s ability to service long-term debt will depend on its long-term business prospects, which are less certain. A popular variable for consideration when analyzing a company’s D/E ratio is its own historical average.
A lower D/E ratio suggests the opposite – that the company is using less debt and is funded more by shareholder equity. However, if the company were to use debt financing, it could take out a loan for $1,000 at an interest rate of 5%. There are various companies that rely on debt financing to grow their business.

